z factor chart for pipette calibration|how to check pipette accuracy : import An experienced and properly trained technologist is required to accurately perform calibration of MLA Pipettes, using the gravimetric method. All procedures are to be performed under controlled environmental conditions (see Section III). . Z Factor Chart Barometric Pressure mm Hg 600 640 680 720 760 800 mbar 800 853 907 960 1013 1067 Q: How does an autoclave work? A: Autoclaves use extreme heat in the form of pressurized steam in order to sterilize goods. Similar to a pressure cooker, an autoclave uses .
{plog:ftitle_list}
A simple, non-illuminated plug & play isolation system that attaches to your .
generate the Z factor, applied in the calculation of the volume of water, and compared with the theoretical volume, which finally determines the accuracy of the pipette.Pipette Calibration Table of Z-Factors. From: Pipette Performance Check. Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene, ESS INO GENOP 200, Revision 1, January, 2001.
to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of water. Then the calculated volume of water is compared with the theoretical volume to determine the accuracy and precision of the pipette. 2. Material and equipment: (1) pipette and tips (2) 50 ml beaker and plastic medicine cup (3) distilled water ( >=10MQ ) (4) temperature meter ( ±0.1℃ )An experienced and properly trained technologist is required to accurately perform calibration of MLA Pipettes, using the gravimetric method. All procedures are to be performed under controlled environmental conditions (see Section III). . Z Factor Chart Barometric Pressure mm Hg 600 640 680 720 760 800 mbar 800 853 907 960 1013 1067of water and air. This correction factor is called the Z-factor as defined in ISO 8655-6 [2]. Method and Points of Attention The new ISO/IEC 17025:2017 is even more particular than the 2005 version about the prior arrangements to be fixed with the customer. Calibrations need to meet the customer requirements whenever possible. There are a few .to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of water. Then the calculated volume of water is compared with the theoretical volume to determine the accuracy and precision of the pipette. 2. Material and equipment: (1) pipette and tips (2) 50 ml beaker and plastic medicine cup (3) distilled water ( >=10MQ ) (4) temperature meter ( ±0.1℃ )
Pipette Calibration Table of Z-Factors From: Pipette Performance Check. Wisconsin State Laboratory of Hygiene, ESS INO GENOP 200, Revision 1, January, 2001. Temperature (°C) Z-Factor 15 1.0019 15.5 1.0020 16 1.0021 16.5 1.0022 . 22.5 1.0034 23 1.0035 23.5 1.0036 24 1.0037 24.5 1.0038 25 1.0039 . Title: Microsoft Word - Table of ZFactors.doc .A new 5-place analytical balance with a pipette calibration kit (Fig.1) and an Artel PCS®3 Pipette Calibration System (Fig. 2) were studied to determine their performance capabilities in calibrating pipettes. Several tests were conducted to evaluate the sources of uncertainty associated with both pipette calibration systems and theTo eliminate the risk of contamination, each pipette is fitted with a tip ejector system. To release the tip, point the pipette at suitable waste receptacle and press the tip ejector with your thumb. B 4. Pers onalized Name Card/Safety Label You can mark the pipette application, your initials, the calibration date, etc. on the safety label.
Perform the calibration by using different set volumes of 100 µl, 500 µl and 1000 µl for 1000 µl pipette (Refer Table-1). Calibration by using different set volumes of 10 µl, 50 µl and 100 µl for 100 µl pipette (Refer Table-2) . (Weight of water x Z factor (1.004 µl/mg) TEST RESULTS. Average Volume : Standard Deviation :Gravimetric analysis for pipette calibration entails dispensing samples of distilled water into a receiving vessel in a precision analytical balance. The density of water is a known constant, the temperature, barometric pressure and humidity are recorded (the Z-factor used in the final mass calculation) and kept within certain limits and thus .2.1 Estimation of the Z factor The Z factor is not just equal to the density of liquid adjusted to the local temperature and pressure. It also takes into account the air density and density of weights used to calibrate the balance. Z factor is calculated as Z=[(1 𝜌𝐿−𝜌 )(1−𝜌 𝜌 )] (3) Where
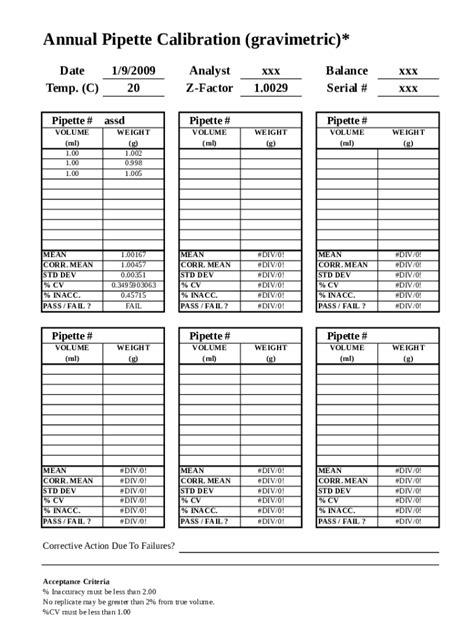
pipette calibration worksheet
Pipettes are a type of lab equipment used to measure and transfer very small volumes of liquid. Accuracy and precision in pipette measurement are necessary as any discrepancy in volumes dispensed can affect the results of an experiment. To ensure accuracy, it is necessary to check the pipette calibration every few months.A new 5-place analytical balance with a pipette calibration kit (Fig.1) and an Artel PCS®3 Pipette Calibration System (Fig. 2) were studied to determine their performance capabilities in calibrating pipettes. Several tests were conducted to evaluate the sources of uncertainty associated with both pipette calibration systems and the
Bias, Uncertainty and Transferability in Standard Methods of Pipette Calibration ARTEL Page 2 Comparison of Gravimetric Standards This section compares and contrasts the two most widely used current standards for pipette calibration using the gravimetric method, ASTM E 1154 (1997) and the newe r ISO 8655-6:2002. It also presents an overview of
pipettes should be checked for accuracy and precision at specified, periodic intervals, depending upon how pipettes are stored, han-dled, and used in the laboratory. 100% 95% 90% 85% 80% Figure 3. Calibration Frequency for Pipettes, Based on Target Reliability Level and Estimated MTBF Table 1: Factors Contributing to MTBF for Mechanical Action .
TABLE 1. Values of the conversion factor Z . Pipettes calibration by the gravimetric method is t he best suited for measuring the performance . of pipettes within the variab le volume .
On INTEGRA's electronic pipettes you can set a calibration reminder either in days or cycles. . (µl) using the Z factor. A corresponding table can be downloaded from the download section on the INTEGRA website. V i = Single volume in µl m i = Single weighing in mg Z = Z Factor V i = m i x Z 2. Calculate the mean volume per test volume and . Convert balance readings (mg) to volume (µl) using the Z factor (table to determine the correct Z factor): V i = Single volume in µl m i = Single weighing in mg Z = Z factor ; Calculate the mean volume per test volume and .relevant standards as well as maintenance & calibration tasks associated with pipettes. Pipette calibration and maintenance should be performed regularly, at minimum annually or more often. The basic requirement for all laboratories to follow is the ISO 8655 standard, which outlines the calibration of pipettes and other piston-
selection of the correction factor Z; see statistical analysis of measurement results). • The pipette is equipped with the appropriate pipette tip, and the pipette tip pre-wetted five times with test liquid to produce a humidity balance in the “dead” air volume. .Pipettes and tips are treated as one system (ISO 8655-2) In the updated ISO 8655-2, the pipette and the pipette tip(s) are considered for calibration together as “one system.” This means a pipette can only be considered calibrated with the tip type used during the calibration. The calibration of pipette is carried out by gravimetric method. When determining the volume of water, the accuracy of measurements is effected by ambient temperature, atmospheric pressure and relative humidity. These factors are usually combined to give the Z factor, used in calculation of volume of water.
the apparatus under test (see Table 1). If the standard uncertainty of measurement of the balance is known (e.g. from the balance calibration certificate), this may be used instead of the repeatability and linearity. The standard uncertainty of measurement shall not be more than two to three times the resolution.For the calibration or adjustment of pipettes, the scales and measuring station should fulfill the following requirements: 1.1 Balances 1.1.1 Balance type Use semi-microbalances and microbalances to calibrate pipettes. Some companies offer balances that are specially designed to meet the requirements of pipette calibration, e.g. Sartorius and .Compare the calculated accuracy and precision with the manufacturer's specifications. If the calculated values are not within specifications, the pipette needs to be calibrated. If the pipette has passed the routine check, it is working as intended. Note: INTEGRA electronic pipettes can be easily calibrated.
Calibration of pipettes using a balance—the gravimetric reference method; Download Now . Products. XPR105MCP Balance for Multichannel Pipette Calibration . The XPR105MCP is the high-speed solution for ISO 8655-compliant calibration of multichannel pipettes. It has a readability of 10 μg and supports mult.in Standard Methods of Pipette Calibration George Rodrigues, Ph.D. . June, 2003 19A4672A . ii Table of Contents . The Z factor is a function of the temperature of the water .Date of Calibration: Calibration due date: Pipet manufacturer: . Z correction factor units: Fixed-Volume Pipette Calibration Reference: ISO 8655-6:2002 (E) Nominal Volume: Mean mass % CV COMMENTS/CORRECTIVE ACTION: PASS/FAIL CV Tolerance RE Tolerance % RE Barometric pressure, kPa or mbar Table 1. Z Correction Factor Table. Temp degrees C Air .
pipette calibration procedure pdf
elisa test questions and answers
elisa test quest diagnostics
elisa test quantitative
pipette calibration excel worksheet
In the soundness test of cement, we determine the amount of excess lime. This test can be conducted by Le-chatelier method and Autoclave Method. Here we will discuss Le-chatlier method of determining the soundness of cement.
z factor chart for pipette calibration|how to check pipette accuracy